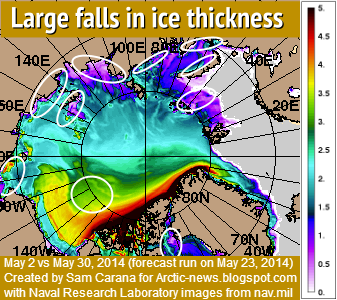
Arctic sea ice has shown large falls in thickness in many areas over the course of May 2014, as shown on above image. The animation below compares the situation between May 2, 2014, and May 30, 2014 (the latter one as forecast by Naval Research Laboratory on May 23, 2014). Ice thickness is in meters.
Thickness is an important indicator of the vulnerability of the ice. If only looking at sea ice extent, one might (wrongly) conclude that sea ice retreat was only minor and that everything looked fine. By contrast, when looking at thickness, it becomes evident that large falls have occurred over the course of May 2014.
Falls at the edges of the sea ice can be expected at this time of the year, but the large fall closer to the center is frightening. On the one hand, it appears to reflect cyclonic weather and subsequent drift of the ice. On the other hand, it also indicates how vulnerable the sea ice has become. Last year, a large area showed up at the center of the sea ice where the ice became very thin, as discussed in July 2013 in the post Open Water at North Pole and again in the September 2013 post North Hole.
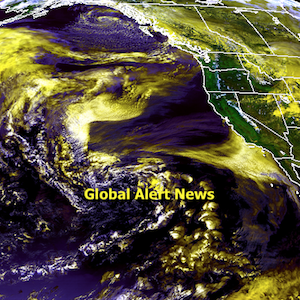
The appearance of huge weak areas at the center of the sea ice adds to its vulnerability and increases the prospect of total sea ice collapse, in case of one or more large cyclones hitting the Arctic Ocean later this year. To highlight the dangerous situation, the main image from a post earlier this month is again added below.
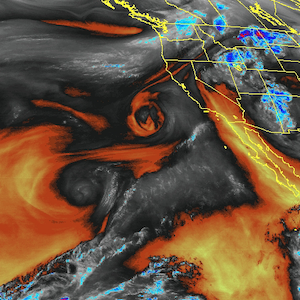
Adding to the concerns are huge sea surface temperature anomalies, as illustrated by the image below, showing anomalies at May 23, 2014, and created by Harold Hensel with ClimateReanalyzer and Google Earth.
 |
| [ click on image to enlarge ] |
Source: Arctic News























































One Response
I cannot tell exactly what these charts mean, but they look creepy. It appears the northern polar ice is moving around. The deep red blobs off the west coast of the US, Canada and just south of Alaska seem glaring. Is that methane levels?